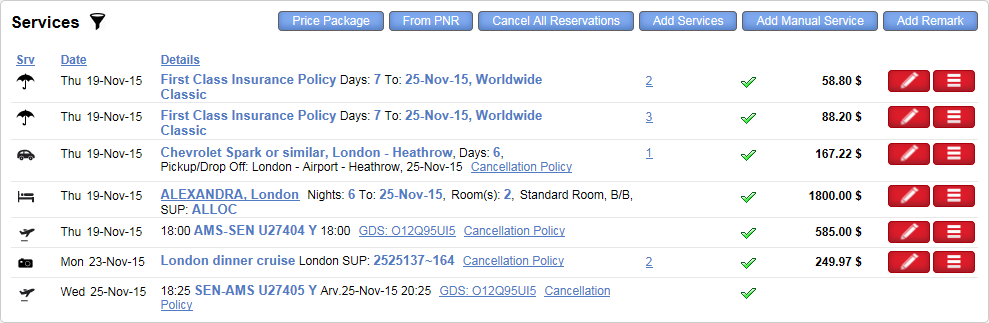

The Services section of the travel file contains all the transactions for services the customer ordered in the travel file.
Transactions can be booked for all passengers or for some of them, and they can contain one service or multiple services, depending on the service type.
Transactions for service can be divided into three categories:
Leg transactions: Leg transactions are transactions for services with legs (segments) (flight, train, transfer and ferry). Each leg is a separate service included in the transaction.
Insurance transaction: Transactions for insurance services belong to a unique category. With insurance transactions, you can add supplements that apply to some but not all of the passengers (for example, only one passenger has a laptop), and the supplements can be reserved for only part of the service duration (for example, when a visit to a ski resort is only three days of a seven day trip).
All other service types: With all other service types, each transaction contains a single service.
Users can open new services for the services they reserve or add them to existing travel files. The services can be reserved from a number of sources:
GDS: Users can create a passenger name record (PNR) in a GDS for flight and hotel reservations. After the PNR is created, the system can automatically import the PNR and create a travel file with the service, or add the service to an existing travel file.
Content interfaces: The system can connect to external third party content interfaces from which users can reserve hotel, activity, car rentals or other travel services.
Internal contracts: Tour operators often negotiate agreements with individual travel suppliers to sell their travel services through the system. These contracts are saved in the Administration Tools, in the Contracts module, and users can reserve these services in the Reservations System. After the user completes the reservation, the reservation can be reported to the supplier (either automatically or manually).
Manual reservation: The user can contact the supplier manually via e-mail or telephone, and receive the relevant information including supplier price. With this information the user can open a manual transaction in the Travel File with all the relevant financial and operational information on the service.
In the travel file, each transaction is comprised of seven tabs containing all the information on the service that was reserved, including general details, pricing information per component and per passenger, reservation status, accounting information, documents that were issued for the service, and relevant notes and remarks on the transaction.
|
Some of the tabs are only relevant for specific service types. |
Service Details: This tab includes general information on the transaction, such as arrival and departure dates and times, supplier information, and reservation status. The information in this tab depends on the service type of the transaction. For example, with flights, you can view information on each leg of the flight, with hotels you can view the board basis, hotel address, and check-in and check-out times, and with cars you can view the SIPP code, category and pick-up and drop off stations.
Passengers & Pricing: This tab lists the passengers and how much the service costs per passenger. In this tab, you can view both the total amount per passenger and also the breakdown according to price component in three prices: net price, supplier price and selling price. Default prices are taken from contracts or interfaces, and with manual transactions the user can manually enter the prices received from the supplier here.
Notes & Remarks: This tab includes internal notes for the user relating to the transaction, and remarks that the user can insert on the various documents issued for the transaction (voucher, reservation, travel file details and itinerary).
Reservations: This tab lists the reservation details of the transaction, including reservation status, reservation number with supplier, reservation details, and dates and times the reservation was reported and confirmed with the supplier.
Accounting: This tab lists the total accounting breakdown of the transaction – the total amounts for the transaction, such as supplier price, net price, selling price, commission, markup and VAT, in two different currencies; the supplier paid and supplier payment method, client payment method, and transaction type; the VAT definitions; general definitions, such as the due date of the voucher; and, agent commission information. In this tab, you can issue a voucher, amend a voucher, and issue refunds from the supplier.
Documents: This tab lists the various documents issued in relation to the transaction – refund, voucher and tax invoice – which you can view. Refunds can be cancelled and approved, and vouchers can be cancelled in this tab.
More Details: This tab lists additional information that can be entered on the transaction, such as trip purpose, budget number, cost center, and project number. With transactions opened for travel agents and corporate clients, unique data saved in the PNR remarks can be mapped to these fields.
Users may enter and edit the information in some of the tabs, all of the tabs, or none of the tabs. This largely depends on how the transaction was made.
Transactions that are created automatically from a GDS or a third party interface do not need to be edited. Vouchers can be issued automatically, and the only reason a user will need to enter the transaction is to issue a refund request if necessary.
Transactions that are created from a contract are initialized with the information from the contract. Users will primarily need to update information in the Reservations tab (and this can be automated), and may edit the information in the Service Details, Passengers & Pricing, Notes & Remarks, Reservations and Accounting tabs if the transaction is amended.
With manual transactions, users will manually need to enter the transaction information in all the relevant tabs.
The following sections will focus in detail on each of the tabs, explain how each tab is used depending on the service type and transaction type, and review the different tasks that can be performed.